”How the Swim Lane Structure Reveals the True Workflow; Value of Swim Lane Analysis in Lean Practice.” In many organizations, leaders and teams believe they have a clear understanding of how work moves from one function to another. Yet, when the entire process is visualized step by step, the reality often surprises them. Hidden delays, unclear responsibilities, repeated checks, and unnecessary handovers become visible almost immediately. One of the most effective tools for revealing these issues is Swim Lane Analysis, a method widely used in lean management and closely aligned with principles found in the Toyota Production System and the broader Toyota Management System.
Swim lane mapping offers a simple but powerful way to observe how work truly flows across departments. It provides a structured view of activities, decision points, and information exchanges, making it easier to understand where inefficiencies occur and how they influence overall performance.
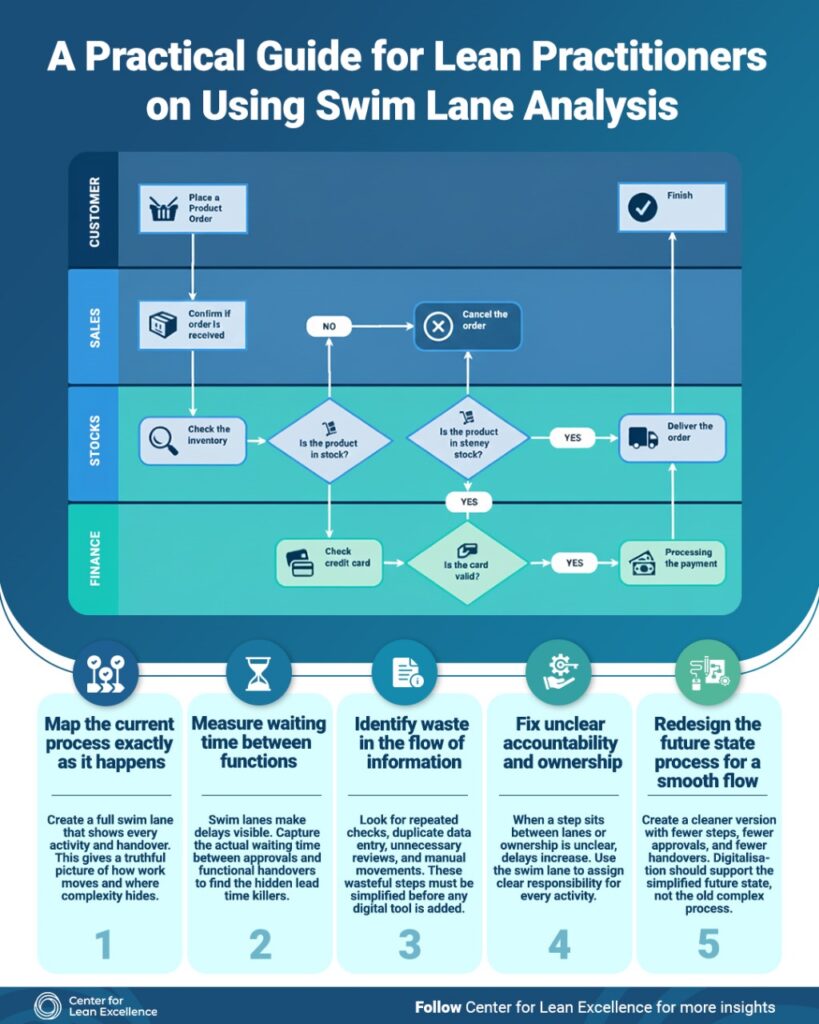
Making the Current State Visible
A central purpose of swim lane analysis is to create a factual picture of the current state of a process. Rather than describing what should happen, the diagram reflects what is actually taking place in daily operations. It identifies each activity, the sequence in which it occurs, and the function responsible.
This form of visualization is important because most operational challenges do not exist within a single step; they arise in the transition between steps. By mapping these transitions clearly, teams gain a more accurate understanding of the entire workflow. The current-state map often reveals inconsistencies, extra approvals, or manual tasks that have become routine but do not add real value.
Understanding Waiting Time and Process Delays
Swim lane analysis also highlights delays that may not be immediately obvious. In many processes, the actual work time is short, but the waiting time between departments is long. These delays accumulate as tasks wait for the next person, system, or decision.
When these moments of inactivity are visualised, organisations can better assess their true lead time. This clarity helps teams pinpoint bottlenecks and evaluate how delays influence overall customer responsiveness. In environments guided by lean principles, particularly those referencing the Toyota Production System, reducing such waiting time is an essential step toward improving flow.
Identifying Waste in the Flow of Information
Much of today’s work involves the movement of information rather than physical materials. Because of this, the flow of information often contains significant waste. Swim lane mapping allows teams to identify patterns such as repeated data entry, manual corrections, unclear communication loops, and unnecessary verification activities.
These issues may seem minor when viewed individually, but their cumulative impact is substantial. By examining the full process, teams can simplify information pathways and create more consistent and reliable workflows. This approach supports operational excellence and prepares organizations for more effective digital transformation efforts.
Clarifying Roles and Responsibilities
Another valuable outcome of swim lane analysis is the clarity it provides regarding ownership. When multiple teams participate in a process, accountability can easily become fragmented. The diagram assigns activities to specific lanes, making it clear who is responsible for what.
This clarity reduces confusion, shortens decision-making time, and improves coordination between functions. It also aligns with the leadership and accountability practices emphasized in the Toyota Management System, where clearly defined roles support effective problem-solving and continuous improvement.
Designing a More Effective Future-State Process
Once the current-state map is understood, organizations can begin to design a future-state version of the process. The goal of this design is not simply to draw a cleaner diagram, but to establish a workflow that is more efficient, more transparent, and easier to manage.
A future-state swim lane typically removes unnecessary steps, reduces handovers, shortens waiting times, and clarifies decision points. Digital tools may be added, but only in ways that support the simplified flow. Rather than digitalizing old inefficiencies, teams create a more effective process first and then use technology to strengthen it.
A Foundational Skill for Lean Practitioners
Swim lane analysis is more than a documentation tool; it is a foundational skill for practitioners working in lean environments. Whether improving a single workflow or aligning with principles found in the Toyota Production System, the method provides a structured way to observe reality and identify improvement opportunities.
By making the invisible visible, swim lane analysis helps organisations understand how work actually flows and where meaningful improvements can be made. It empowers teams to simplify processes, reduce waste, and build more reliable and efficient systems.
As organizations continue to pursue lean transformation and explore structured approaches like the Toyota Production System and Toyota Management System, the ability to understand and redesign process flow becomes essential. Swim lane analysis supports this work by providing a practical, accessible tool that guides teams toward better alignment, smoother workflows, and more consistent outcomes.
In the end, the strength of this method lies in its simplicity:
when the process becomes visible, improvement becomes achievable.

